Rosacea is a chronic skin condition primarily affecting the face, characterized by redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes pustules. This condition can significantly impact self-esteem and lead to emotional stress. This guide provides comprehensive information on rosacea, including its symptoms, causes, and treatment options, helping you better understand and manage this skin condition effectively.
What is Rosacea?
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition marked by redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes inflamed pimples on the face. It commonly affects areas like the cheeks, nose, and forehead. Rosacea is not contagious; it results from an overactive immune system causing rapid skin cell turnover. Understanding this condition is crucial for effective management and treatment.
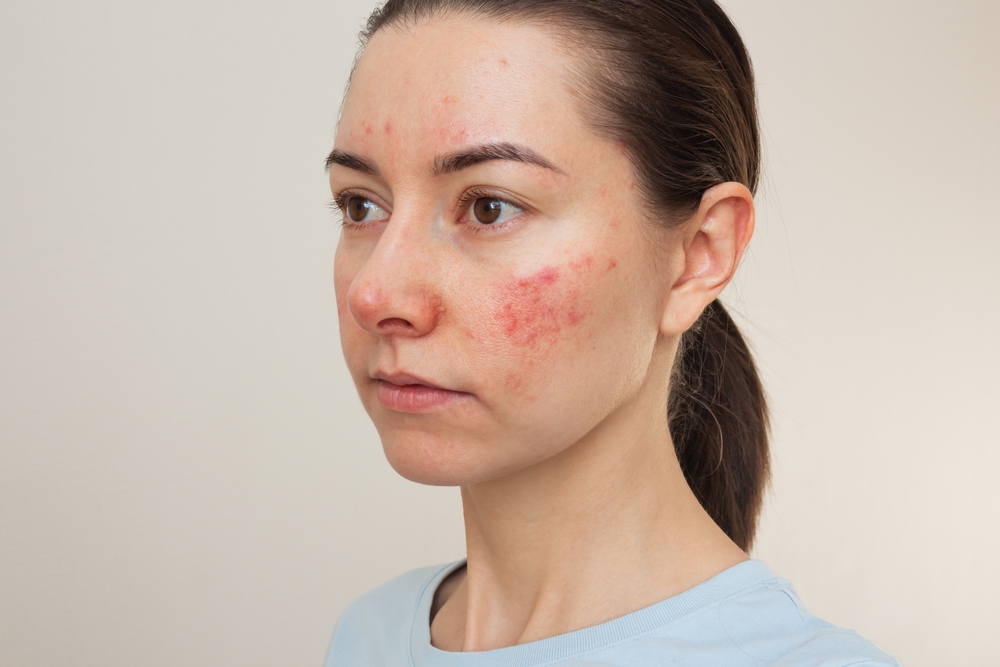

Common Symptoms of Rosacea
Typical symptoms of rosacea include persistent facial redness, visible blood vessels (telangiectasia), and small, red pustules. Some individuals also experience burning or itching sensations. In advanced cases, the skin may thicken and become bumpy. Symptoms can vary in severity and may flare up or improve over time, requiring ongoing management.
Causes and Triggers
The exact cause of rosacea is not fully understood, but genetic and immune system factors are believed to contribute. Known triggers include certain foods and drinks (like alcohol and spicy foods), sun exposure, extreme temperatures, and stress. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Diagnosis: How is Rosacea Identified?
Rosacea is typically diagnosed through a physical examination and patient history. A dermatologist will assess the characteristic symptoms and make a diagnosis based on clinical appearance. In some cases, additional tests may be needed to rule out other skin conditions. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for selecting the appropriate treatment plan.
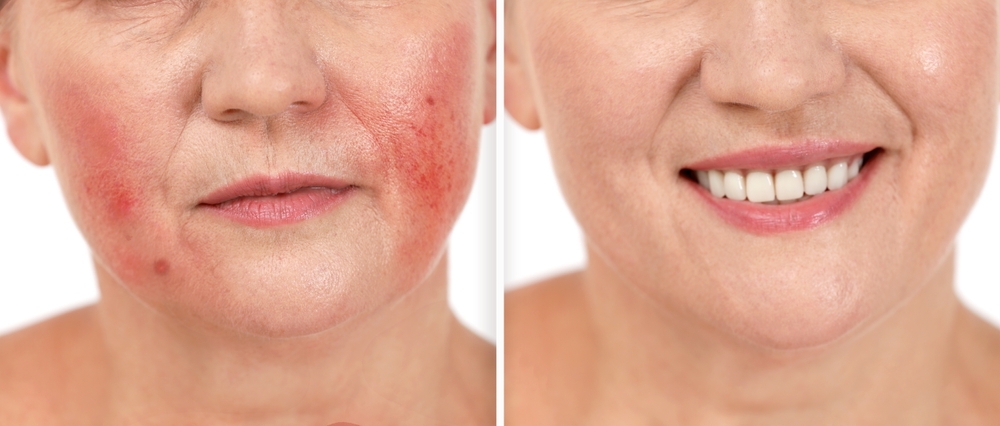
Topical Treatments for Rosacea
Topical treatments are often the first line of therapy for rosacea. These include medications like metronidazole or azelaic acid, which have anti-inflammatory properties and can reduce redness. Topical retinoids and antibiotics may also be prescribed to alleviate symptoms and improve skin condition.
Oral Medications for Rosacea
For more severe cases of rosacea, oral medications may be necessary. These include antibiotics like doxycycline or tetracycline, which help reduce inflammation and pustules. In some cases, other systemic medications might be used to control symptoms effectively and manage the condition.
Lifestyle and Dietary Tips
Lifestyle changes can help manage rosacea symptoms. Avoid known triggers such as spicy foods, alcohol, and hot beverages. Protect your skin from the sun by using sunscreen and wearing protective clothing. Managing stress through relaxation techniques can also be beneficial in reducing flare-ups.

Skincare Routine for Rosacea Patients
A gentle skincare routine is essential for those with rosacea. Use mild, non-irritating cleansers and moisturizers designed for sensitive skin. Avoid abrasive scrubs and products with alcohol or strong fragrances, as they can exacerbate symptoms and cause further irritation.
Environmental Factors’ Impact
Environmental factors such as extreme temperatures, pollution, and sun exposure can worsen rosacea. Protect your skin from harsh weather conditions by wearing appropriate clothing and using protective skincare products. Take extra precautions in extreme temperatures to minimize skin irritation and flare-ups.
Psychological Effects and Coping Strategies
Rosacea can affect self-esteem and emotional well-being. The visible skin condition may lead to stress, embarrassment, or depression. Seeking support from friends, family, or a therapist can help manage the emotional impact and develop coping strategies to improve overall quality of life.

Importance of Regular Medical Check-ups
Regular visits to a dermatologist are important for monitoring rosacea and adjusting treatments as needed. Your doctor can evaluate the severity of the condition, monitor treatment side effects, and ensure that therapies are effective. Ongoing medical care helps in long-term symptom management and maintaining skin health.
Conclusion
Understanding rosacea is crucial for effective management and improving quality of life. This chronic skin condition, marked by facial redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes pustules, requires a comprehensive approach to treatment. By recognizing symptoms, identifying triggers, and following appropriate treatment plans, individuals can manage their condition more effectively. Regular consultations with a dermatologist and adopting lifestyle adjustments can help control flare-ups and maintain skin health. With the right strategies and support, living well with rosacea is achievable.

