Skin diseases are diverse and complex, affecting individuals of all ages and backgrounds. From common conditions like acne to more severe disorders such as psoriasis, understanding the nuances of skin health is crucial. This guide provides a detailed look at various skin diseases, their symptoms, treatments, and preventive measures to help you stay informed and proactive about your skin health.
Understanding Acne: Causes and Treatments
Acne, a prevalent skin condition, stems from pores clogged by oil and dead skin cells, often exacerbated by bacteria. Treatment options range widely, including topical creams that target acne directly and oral medications designed to reduce overall oil production. Strategies often focus on accelerating skin cell turnover to prevent clogging and using antibacterial agents to combat infection, aiming for clearer, healthier skin. These treatments can be tailored to individual needs based on the severity and type of acne.
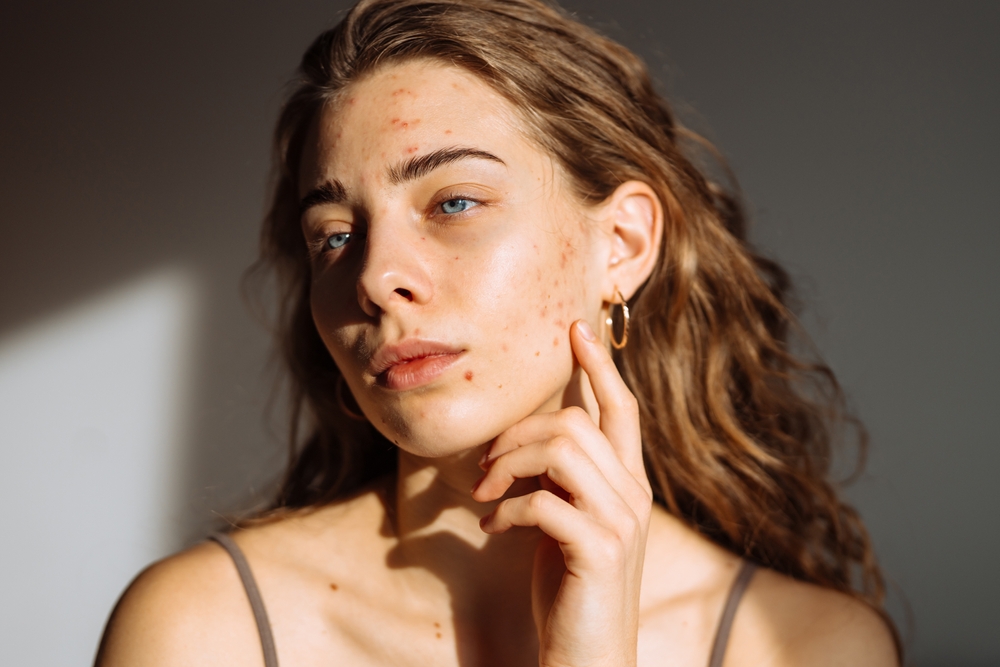

Eczema Explained: Symptoms and Management
Eczema, characterized by itchy, red, and inflamed skin, demands consistent management. Key strategies include regular moisturization to maintain skin hydration, avoiding known irritants and allergens that can exacerbate symptoms, and applying prescribed topical treatments such as creams or ointments. These treatments are crucial for controlling inflammation and alleviating discomfort, helping to soothe the affected areas and prevent flare-ups. Identifying and steering clear of personal triggers is also essential for effective long-term management.
Psoriasis: Beyond the Surface
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that disrupts the normal cycle of skin cell turnover, leading to the rapid buildup of cells on the skin’s surface. This results in thick, scaly patches that can be itchy and painful. Managing psoriasis typically involves a combination of treatments including topical creams to soothe and hydrate the skin, light therapy to slow cell growth, and systemic medications to target underlying inflammation. Each treatment is tailored to the severity and location of the outbreaks to effectively reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.
Rosacea: Identification and Lifestyle Adjustments
Rosacea is marked by persistent redness and visible blood vessels in the face, often exacerbated by triggers such as spicy foods, alcohol, and changes in temperature. Effective management requires identifying and avoiding these triggers to reduce flare-ups. Protecting the skin from sun exposure with the use of broad-spectrum sunscreen and wearing protective clothing are also vital. For some, medications may be necessary to control inflammation and redness. Regular consultations with a dermatologist can help tailor treatment to individual needs.
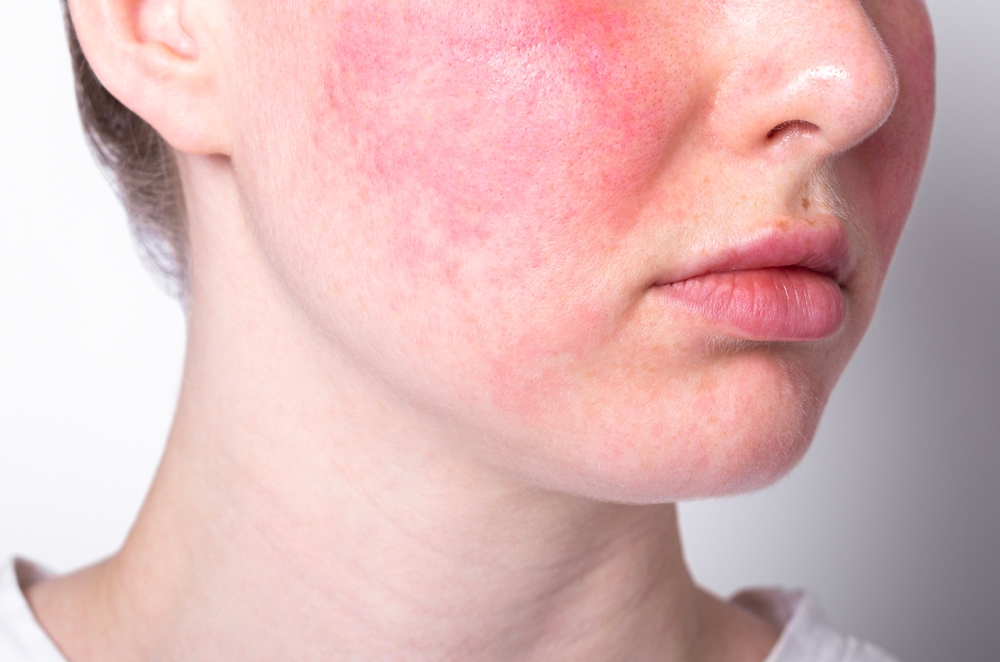
Skin Cancer: Types, Signs, and Prevention
Skin cancer stands as one of the gravest skin conditions, encompassing types like melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. Prevention is crucial and involves using broad-spectrum sunscreen to shield skin from harmful UV rays, wearing protective clothing that covers as much skin as possible, and engaging in regular skin checks by a healthcare professional to catch any early signs of cancer. These proactive steps are essential for minimizing risk and ensuring early detection and treatment, which significantly improve outcomes.
Hives (Urticaria): Triggers and Treatments
Hives, or urticaria, are red, itchy welts that can suddenly emerge on the skin, often triggered by allergies, stress, or reactions to medications. The primary treatment involves antihistamines, which help reduce itching and swelling. Identifying and avoiding known triggers is also crucial to prevent future episodes. For persistent cases, a healthcare provider might prescribe stronger treatments. Lifestyle adjustments and stress management techniques can also be beneficial in managing hives effectively.
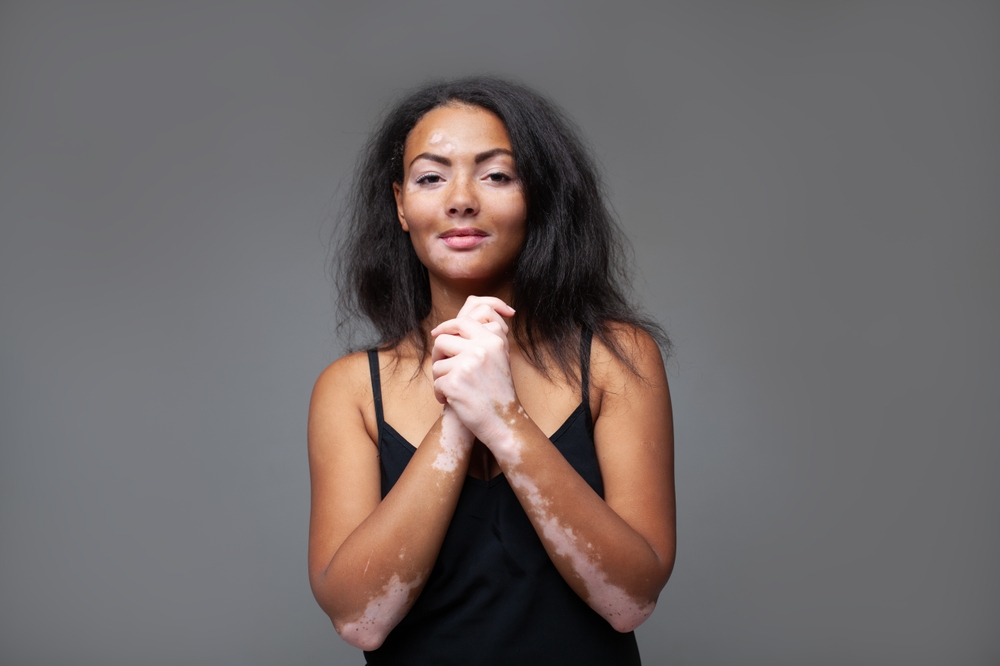
Vitiligo: Understanding Pigment Loss
Vitiligo is characterized by the loss of skin pigment, leading to distinct white patches on the body. Although currently incurable, several treatments can manage its appearance effectively. Light therapy helps stimulate pigment cells in affected areas, while topical corticosteroids can reduce inflammation and possibly restore some pigment. Additionally, skin camouflage products can temporarily cover the patches, improving cosmetic appearance. For those seeking more permanent solutions, options like skin grafts or tattooing might be considered in consultation with a dermatologist.

Fungal Infections: Common Types and Cures
Fungal infections can impact different areas of the body, manifesting symptoms such as itching, redness, and scaling. Treatment primarily involves the use of antifungal creams applied directly to the affected areas to target the fungus locally. For more widespread or resistant infections, oral antifungal medications may be prescribed to tackle the fungus systemically. Maintaining good hygiene and keeping affected areas dry and clean are also important preventive measures to help manage and eliminate fungal infections effectively.
Impetigo: Contagious Infections Explained
Impetigo is a highly contagious bacterial infection particularly common among children, characterized by red sores or blisters that can rupture and form a honey-colored crust. The primary treatment involves antibiotic ointments applied directly to the lesions to control the infection and prevent its spread. In cases where the infection is more widespread or severe, oral antibiotics may be necessary. Good hygiene practices, such as washing hands frequently and keeping nails trimmed, are also crucial in preventing the spread of impetigo.
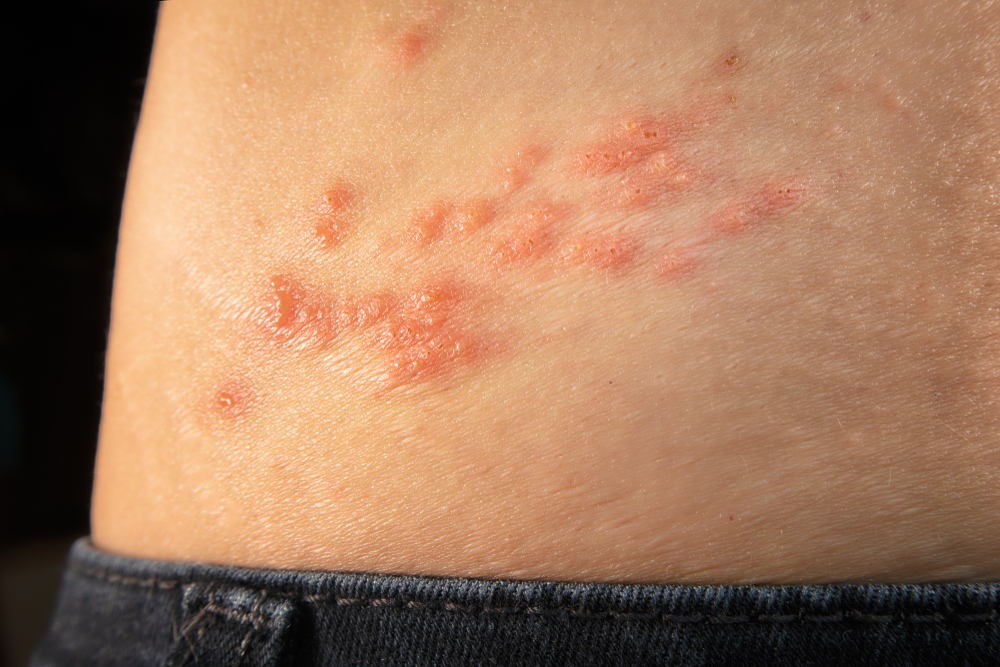
Shingles: Symptoms and Vaccine Information
Shingles, caused by the reactivation of the chickenpox virus (varicella-zoster), leads to painful rashes and blisters typically on one side of the body. The most effective prevention method is vaccination, which can significantly reduce the risk of developing shingles and its complications. If shingles does occur, prompt treatment with antiviral medications is crucial. These medications can help reduce the pain, decrease the severity, and shorten the duration of the disease. Managing pain with medications and home care remedies is also important for comfort and recovery.
Preventive Skincare: Daily Routines and Tips
Maintaining healthy skin is a holistic process that extends beyond merely treating existing conditions. It involves establishing a daily care routine that includes the application of sunscreen to protect against harmful UV rays, using gentle cleansing products to avoid irritation, and ensuring the skin is adequately hydrated. These practices help to preserve the skin’s natural barrier, prevent damage, and keep the skin looking and feeling healthy. Additionally, adopting a balanced diet and staying hydrated can further enhance skin health from the inside out.

